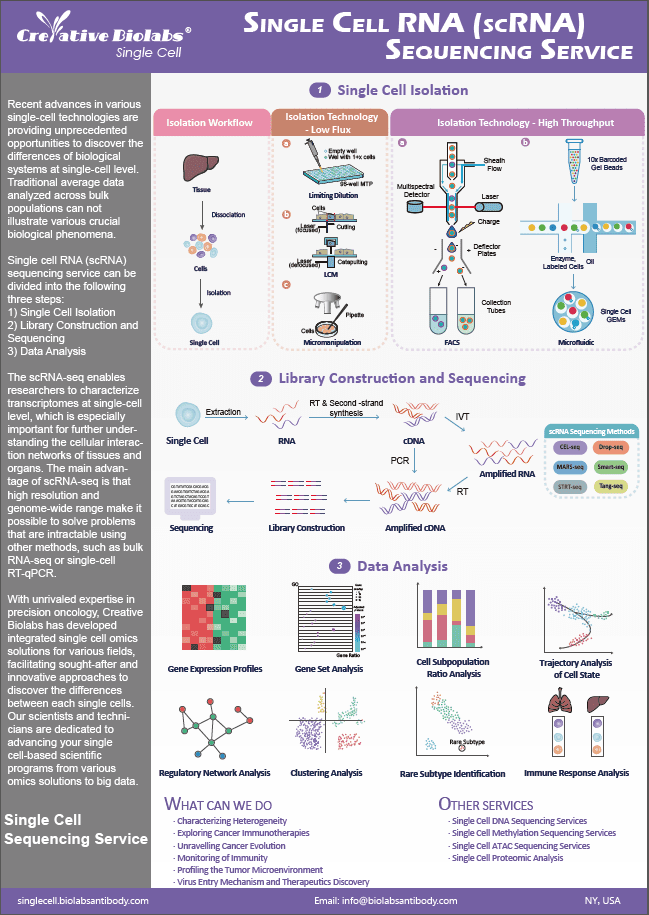
miRNA Array Service
miRNA (micro-RNA) arrays can detect mature miRNAs and differentiate highly similar miRNA molecules. It is widely used for detecting and comparing the expression status of microRNAs in different samples and for analyzing the target genes they regulate.
Overview of miRNA
The microRNA, often known as miRNA, is a vast family of RNA molecules that are around 22 nucleotides long and are widely expressed in eukaryotic organisms. There are at least hundreds of microRNAs that are encoded in complex genomes. These microRNAs are principally responsible for inhibiting the expression of the target post-transcriptional gene. A growing body of evidence suggests that microRNAs play crucial roles in normal cellular processes (differentiation, proliferation, and cell death) and the stress response. This evidence also suggests that microRNAs are involved in developing cancer and other pathological conditions. Because of this, microRNAs have the potential to act as a diagnostic and prognostic tool for illnesses. Therefore, it is necessary to have a solid understanding of the expression of miRNAs as well as their functions in a variety of diverse environments.
 Fig. 1 miRNA biogenesis and mode of action.1, 4
Fig. 1 miRNA biogenesis and mode of action.1, 4
Functions of miRNA
The RNA-induced silencing complex is responsible for miRNAs' regulatory actions (RISC). MiRNA forms complexes with RISC, activating the complex to target messenger RNA (mRNA) designated by miRNA. Numerous models of RISC assembly have been presented, and researchers continue to investigate the mechanisms of RISC loading and activation. The degree and form of complementarity between the miRNA and its target dictate the gene silencing mechanism, slicer-dependent mRNA degradation, or slicer-independent translation inhibition.
 Fig. 2 The RISC loading complex containing mature miRNA translocates to a P-body compartment specific for RISC assembly and activation.2, 4
Fig. 2 The RISC loading complex containing mature miRNA translocates to a P-body compartment specific for RISC assembly and activation.2, 4
Published Data
| Paper Title | Microarray profiling of miRNA and mRNA expression in Rag2 knockout and wild-type mouse spleens |
| Journal | Scientific Data |
| Published | 2018 |
| Abstract | Biomedical research often uses the Rag2 knockout (KO) mouse. The immunologically impaired state concurrently affects several signaling channels and molecules, including miRNAs and mRNA transcripts that are engaged in essential biological activities. In addition, miRNAs and transcripts are interdependent, often creating a feedback loop; dysregulation in one can influence the expression of the other, and both participate in many physiological processes including immune control. They present a comprehensive dataset comparing Rag2 KO mice to wild-type mice in miRNA and mRNA expression. The miRNA and mRNA expression profiles were obtained from whole RNA using a miRNA expression microarray or a BeadChip microarray, respectively. Hence, this dataset will offer the framework for a comparative examination of the miRNAs and mRNAs that are dysregulated in Rag2 KO mice. The results should reveal how miRNAs regulate immune function and interact with mRNAs in Rag2 KO mice. |
| Result | The expression of twenty-eight microRNAs and 936 genes varied by at least twofold between Rag2 KO mice and their wild-type counterparts. qRT-PCR was used to check the expression of these differentially expressed miRNAs and genes in order to verify the validity of these microarray studies. For these experiments, a second group of Rag2 KO and wild-type mice were employed; these mice were maintained and grown under the same experimental circumstances as the animals used for the microarray analysis of miRNA expression and the BeadChip microarray analysis. |
Our miRNA Array Services
Real-time PCR, microarrays, and deep sequencing have been used extensively to profile miRNA expression. Among these, the miRNA microarray technique is widely utilized since it is high throughput, generally less expensive, and most of the experimental and analysis steps can be performed in the molecular biology laboratories of the majority of universities, medical schools, and affiliated institutions. However, the prefabricated miRNA microarray cannot suit the individual needs of researchers doing an in-depth analysis of miRNAs. As a renowned biotechnology firm, Creative Biolabs possesses vast knowledge and experience that enables it to deliver unique and tailored miRNA microarray services.
 Fig. 3 Overview of the miRNA microarray procedure. 3. 4
Fig. 3 Overview of the miRNA microarray procedure. 3. 4
Creative Biolabs' mission is to offer you the most cost-effective and high-quality bespoke miRNA microarray solutions to assure your complete happiness.
For any information, please contact us.
Features & Benefits
-
Comprehensive miRNA Profiling
The miRNA Array Service provides detailed profiling of miRNAs across various biological samples, including tissues, cell lines, and bodily fluids. This comprehensive analysis allows researchers to identify and quantify miRNAs, offering critical insights into their roles in disease mechanisms and therapeutic potential. -
High Sensitivity and Specificity
Utilizing advanced array technology, the service ensures high sensitivity and specificity in miRNA detection. Accurate detection and quantification of miRNAs enable researchers to confidently identify miRNA biomarkers and therapeutic targets, ensuring reliable research outcomes. -
Functional Annotation
The service includes detailed functional annotation of miRNAs, highlighting their target genes and regulatory pathways. Understanding these interactions helps researchers uncover the regulatory roles of miRNAs, providing insights into gene regulation mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. -
High Throughput and Efficiency
Designed for high-throughput analysis, the miRNA Array Service can process large numbers of samples efficiently. This high throughput capability makes it ideal for large-scale studies, enabling researchers to generate extensive data sets quickly and cost-effectively. -
Discovery of Novel miRNAs
The high-resolution arrays can detect previously uncharacterized miRNAs, expanding the catalog of known miRNAs. Discovering novel miRNAs opens up new research avenues and potential therapeutic applications, contributing to a deeper understanding of miRNA functions and their impact on health and disease.
Q&As
Q: What types of samples can be analyzed using the miRNA Array Service?
A: The miRNA Array Service is versatile and can analyze a wide range of sample types, including tissues, cell lines, and bodily fluids such as blood, serum, and plasma. This flexibility allows researchers to study miRNA expression in different contexts and disease models, providing comprehensive insights into their roles across various conditions.
Q: What kind of data analysis is provided with the miRNA Array Service?
A: The miRNA Array Service includes comprehensive data analysis, such as differential expression analysis, clustering, and pathway enrichment analysis. Researchers receive detailed reports highlighting significant changes in miRNA expression and their potential biological implications, facilitating the discovery of new therapeutic targets and biomarkers.
Q: How does the miRNA Array Service ensure data reproducibility and reliability?
A: The service employs robust protocols for RNA extraction, labeling, and hybridization, along with stringent quality control measures. This ensures high reproducibility and reliability of the data, providing researchers with consistent and accurate results for their studies.
Q: How does the miRNA Array Service ensure high sensitivity and specificity in miRNA detection?
A: The service employs advanced array technologies that utilize highly specific probes to detect miRNAs with high sensitivity. This ensures accurate quantification and dentification of miRNAs, which is crucial for reliable research outcomes and for identifying potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Q: How can the miRNA Array Service be used to study the impact of miRNAs on gene expression regulation?
A: The service can profile miRNAs and their target mRNAs in the same samples, providing insights into how miRNAs regulate gene expression. This information helps researchers understand the post-transcriptional regulatory networks controlled by miRNAs and their impact on cellular functions.
Resources
References
- Chaudhary, Saurabh et al. "MicroRNAs: Potential Targets for Developing Stress-Tolerant Crops." Life (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 11,4 289. 28 Mar. 2021, doi:10.3390/life11040289.
- Macfarlane, Leigh-Ann, and Paul R Murphy. "MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer." Current genomics vol. 11,7 (2010): 537-61. doi:10.2174/138920210793175895
- Reza, Abu Musa Md Talimur et al. "Microarray profiling of miRNA and mRNA expression in Rag2 knockout and wild-type mouse spleens." Scientific data vol. 5 170199. 9 Jan. 2018, doi:10.1038/sdata.2017.199
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Search...