circRNA Array Service
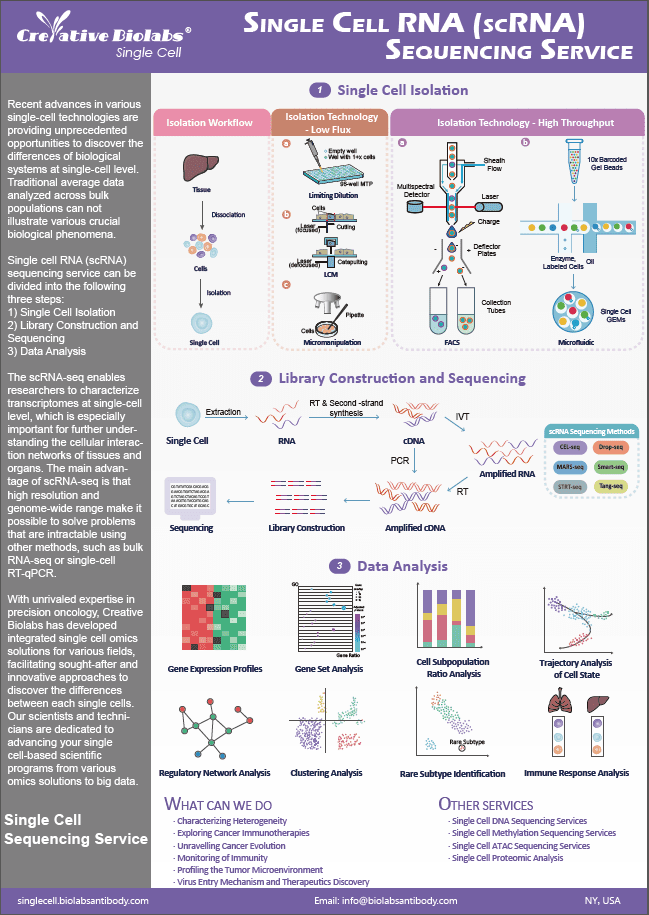
circRNA array is a method for profiling and analyzing circular RNAs in organisms. Circular RNA (circRNA) is a unique type of RNA that, in contrast to linear RNA, forms a covalently closed continuous loop, some of which are relatively abundant in the eukaryotic transcriptome. The majority of these circRNAs are derived from exonic or intronic sequences, are conserved between species, and frequently exhibit tissue/developmental stage-specific expression. Due to their greater nuclease stability, circular RNAs are more stable than linear RNAs, which represents a tremendous therapeutic advantage as a unique class of biomarkers. In addition, it has been demonstrated that circRNAs operate as natural miRNA sponge transcripts, also known as competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs), in numerous species. Their interaction with illness-related miRNAs highlights the potential role of circular RNAs in disease regulation.
Functions of circRNA
Some circRNAs may have important non-coding functions that are related to how stable they are. This is because the third position of codons, which is usually not very stable because the genetic code is redundant, is more stable in some circRNAs than in exons that are not part of circRNAs. But only a small number of those that are thought to work as miRNA sponges have had their biological functions researched. Crosslinking immunoprecipitation data sets also show that circRNAs interact with many RNA-binding proteins to act as protein sponges, improve protein function, act as scaffolds to help enzymes and substrates form complexes, and bring proteins to specific sites. Also, even though most circRNAs are thought to be non-coding, a small number of them can translate without a cap in some situations.
Published Data
| Paper Title | Targeting mitochondria-located circRNA SCAR alleviates NASH via reducing mROS output |
| Journal | Cell |
| Published | 2020 |
| Abstract | Immunometabolic diseases involve mitochondria's genome. Without a delivery system, mitochondria-located noncoding RNAs' functions are unknown. They found that mitochondrial circRNAs make up a significant portion of downregulated circRNAs in liver fibroblasts of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients. Using mitochondria-targeting nanoparticles, they found that Steatohepatitis-associated circRNA ATP5B Regulator (SCAR) in mitochondria inhibits mitochondrial ROS (mROS) output and fibroblast activation. PGC-1a-mediated circRNA SCAR binds to ATP5B and blocks CypD-mPTP interaction, shutting down mPTP. ER stress-induced CHOP inhibits PGC-1a in lipid overload. Targeting circRNA SCAR reduces high-fat diet-induced cirrhosis and insulin resistance in vivo. circRNA SCAR promotes steatosis-to-NASH progression. They identify a mitochondrial circRNA that drives metaflammation and targets NASH treatment. |
| Result | They compared the profiles of circRNA expression in primary fibroblasts from four patients with NASH cirrhosis and four patients without NAFLD. In NASH fibroblasts, 15 circRNAs were consistently upregulated and 11 were consistently downregulated. Four out of eleven downregulated circRNAs were surprisingly encoded by the mitochondrial genome, despite nuclear circRNAs comprising the vast majority of the entire circRNomics. The suppression of three mitochondrial circRNAs (mito-circRNAs) in NASH patients was validated by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) in a separate cohort of 18 patients with NASH cirrhosis and 20 patients without NAFLD. These 3 mito-circRNAs are generated from the mitochondrial genome via a "back-splicing" mechanism, as shown by the fractionation experiment. Despite hsa_circ_0089763 retaining an intron between exons, all mature transcripts contain exonic sequences. hsa_circ_0089762 and hsa_circ_0089763 are produced from the light strand of mito-DNA, whereas hsa_circ_0008882 is produced from the heavy strand. |
Creative Biolabs provides a platform for profiling, analyzing, and exploring this new and interesting world of non-coding RNAs by systematically evaluating the expression of circRNAs. From sample to publishable data, we provide specialist circRNA array services. For more information, please contact us.
circRNA Array Services
Creative Biolabs provides a platform for profiling, analyzing, and exploring this new and interesting world of non-coding RNAs by systematically evaluating the expression of circRNAs. From sample to publishable data, we provide specialist circRNA array services. For more information, please contact us.
Features & Benefits
-
Comprehensive Profiling
The circRNA Array Service offers detailed profiling of circular RNAs across various biological samples, including tissues, cell lines, and bodily fluids. This comprehensive analysis enables researchers to identify and quantify circRNAs, providing critical insights into their roles in different diseases and biological processes. -
High Specificity and Sensitivity
The service uses RNase R treatment to enrich circRNAs by degrading linear RNAs, coupled with high-resolution array technology targeting circRNA-specific junctions. This approach ensures high specificity and sensitivity, allowing accurate detection and quantification of circRNAs, which is crucial for reliable research outcome. -
Versatile Sample Compatibility
The circRNA Array Service can analyze various sample types, including tissues, cell lines, and bodily fluids like blood and serum. This versatility allows researchers to study circRNA expression in different contexts and disease models, providing comprehensive insights into their roles across various conditions. -
High Throughput and Efficiency
The circRNA Array Service is designed for high-throughput analysis, capable of processing large numbers of samples efficiently. This high throughput capability makes it ideal for large-scale studies, enabling researchers to generate extensive data sets quickly and cost-effectively. -
Enhanced Biomarker Discovery
The service identifies differentially expressed circRNAs that can serve as potential biomarkers for various diseases. These biomarkers can be used for early disease diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring treatment responses, aiding in the development of personalized medicine approaches.
FAQs
Q: What does the circRNA Array Service offer?
A: The circRNA Array Service provides comprehensive profiling and analysis of circRNAs in biological samples. This service includes RNA isolation, quality control, RNase R treatment to enrich circRNAs, cDNA synthesis, labeling, array hybridization, and detailed data analysis. This end-to-end service ensures accurate identification and quantification of circRNAs, providing valuable insights for research and development projects.
Q: What types of samples can be analyzed using the circRNA Array Service?
A: The circRNA Array Service can analyze various biological samples, including tissues, cell lines, and bodily fluids (e.g., blood, serum, plasma). This versatility allows researchers to study circRNA expression in different contexts and disease models, providing comprehensive insights into their roles across various conditions and biological processes.
Q: How does the circRNA Array Service enhance cancer research?
A: CircRNAs have been implicated in cancer progression, metastasis, and drug resistance. The circRNA Array Service helps identify differentially expressed circRNAs in tumor versus normal tissues, uncovering potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. By understanding circRNA profiles, researchers can develop strategies to modulate their expression and improve cancer treatment outcomes.
Q: What kind of data analysis is provided with the circRNA Array Service?
A: The service includes comprehensive data analysis, such as differential expression analysis, hierarchical clustering, and functional annotation. Researchers receive detailed reports highlighting differentially expressed circRNAs, their potential miRNA binding sites, and associated pathways. This data helps in understanding the biological roles of circRNAs and their implications in various diseases.
Q: What are the quality control measures implemented in the circRNA Array Service?
A: The circRNA Array Service incorporates several quality control (QC) measures to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. These measures include assessing the purity and concentration of total RNA, evaluating RNA integrity, and using RNase R treatment to enrich circRNAs by degrading linear RNAs. Additionally, rigorous QC steps are applied during cDNA synthesis, labeling, array hybridization, and data extraction to ensure high specificity and sensitivity in detecting circRNAs.
Resources
Search...