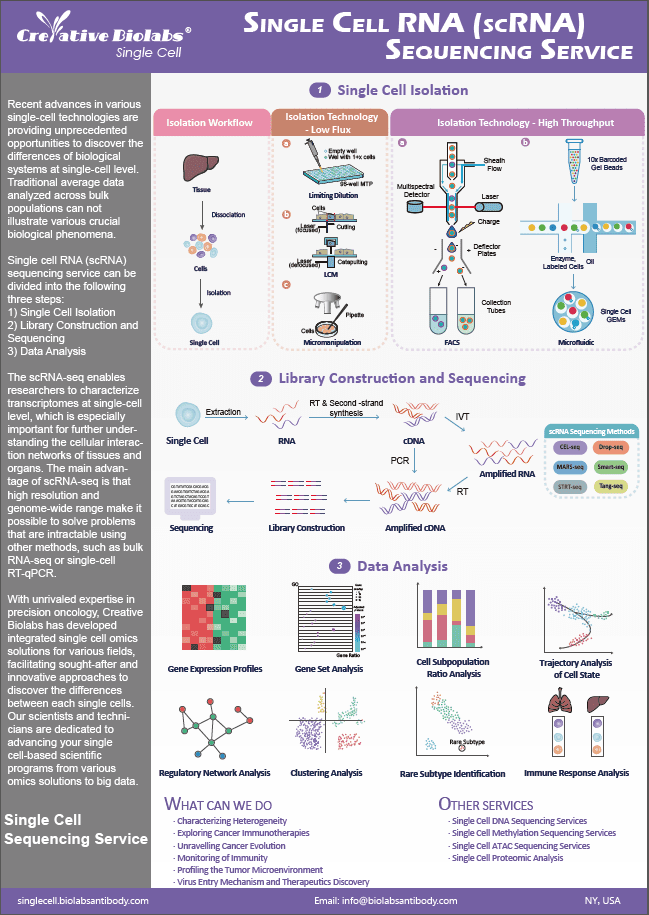
- Home
- Single Cell Featured Services
- Single Cell Metabolomics Services
- Single Cell Energy Metabolism Profiling
Single Cell Energy Metabolism Profiling Service
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive range of customized, high-quality services in single cell energy metabolism profiling service to help researchers study metabolic responses in multiple cell types and study energetic metabolism reprogramming in cancer and immune responses.
Energy Metabolism
Energetic metabolism comprises a series of interconnected biochemical pathways capable of using energy-rich molecules to produce ATP (Argüello, 2020). ATP can be produced by oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) or glycolysis in cells. Aerobic glycolysis promotes cell proliferation, and in hypoxic conditions, it can help cells survive. Immune cells can migrate into peripheral tissues and adapt to changes in the microenvironment. Their energy metabolic profile is linked to microanatomical localization, activation, proliferation, and functional status (Argüello, 2020). The study of energy metabolism can help researchers to evaluate biological function in both health and disease.
Single Cell Energy Metabolism Profiling Method
The protein synthesis (PS) machinery immediately consumes almost half of the total energy that mammalian cells create by degrading glucose, amino acids, and/or lipids. The high energy cost of this important metabolic process provides a methodological opportunity to use PS levels as a measure of global metabolic activity. SCEMFC (single cell energetic metabolism by flow cytometry): a flow cytometry-based method to functionally profile energy metabolism with single-cell resolution. We paired a novel antipuro monoclonal antibody with the drug puromycin(puro), whose incorporation is a reliable readout for assessing PS levels in vitro and in vivo, to establish a simple method for complicated metabolic profiling with single-cell resolution based on PS levels as the readout. The profile reveals the metabolic capacities and dependencies of the cells and high glycolytic capacity profile.
Cell sorting and incubation with cell culture can affect the metabolic activity of the cells, so metabolic profiles of heterogenous and scarce living cell populations derived from human blood samples or biopsies, ex vivo cannot be established. SCEMFC: a method for determining metabolic capacities and dependencies of cells regardless of their phenotype. Here is a comparative table of methods for profile metabolism.
Our Single Cell Energy Metabolism Profiling Service
We offer scientific and meticulous design for sample preparation and divide it, then treat each with the inhibitors (e.g., DG, O, DG+O, H) and puro. After staining and flow cytometry, the profile of response of the different cell subsets is analyzed. The profile reveals the metabolic capacities and dependencies of the cells and high glycolytic capacity profile.
 Fig.1 Our Single Cell Energy Metabolism Profiling Service. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.1 Our Single Cell Energy Metabolism Profiling Service. (Creative Biolabs)
Applications
SCEMFC technology can determine the energy state of each immune cell or cancer cell in a tumor, as well as their energy source and metabolic pathways. We hope that researchers can use this new technology to conduct relevant clinical trials and learn more about how it might be used to predict patient response to therapy.
Professional consultation provides guidance before, during and after the project. please contact us for your tailored solution about single cell energy metabolism profiling.
Features
-
High Sensitivity and Resolution
Our service offers high sensitivity to detect subtle changes in single-cell energy metabolism, providing detailed insights into metabolic pathways.
-
Comprehensive Metabolic Analysis
We provide comprehensive analysis of key metabolic parameters such as ATP production, glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and metabolite levels at the single-cell level.
-
Quantitative Assessment
Precise quantification of metabolic fluxes and metabolic intermediates within individual cells, enabling accurate characterization of metabolic profiles.
-
Cellular Heterogeneity Analysis
Identify metabolic differences among heterogeneous cell populations within tissues or samples, crucial for understanding cellular function and disease mechanisms.
-
Time-course Studies
Capability for time-course studies to observe dynamic changes in cellular metabolism over time, essential for studying metabolic responses to stimuli or treatments.
Q&As
Q: What are the applications of Single Cell Energy Metabolism Profiling in immunology?
A: This profiling can assess the metabolic states of immune cells, aiding in the study of immune responses and diseases. It helps in understanding how immune cells alter their metabolism during activation and function.
Q: How does Single Cell Energy Metabolism Profiling aid in drug development?
A: By understanding the metabolic dependencies of different cell types, researchers can identify potential drug targets and evaluate the efficacy of metabolic inhibitors in a cell-specific manner.
Q: Why is single-cell analysis important compared to bulk analysis?
A: Single-cell analysis uncovers the heterogeneity within cell populations, revealing variations that bulk analysis may miss. This is crucial for understanding diseases where cellular behavior is not uniform.
Q: What sample types can be analyzed using this service?
A: Samples like human blood, biopsies, and solid tumor tissues can be analyzed. The method is particularly useful for rare cell populations that are difficult to study using traditional methods.
Q: How does Single Cell Energy Metabolism Profiling contribute to understanding metabolic diseases?
A: This service provides detailed insights into the metabolic dysfunctions at the cellular level, which is essential for understanding diseases like diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndromes. It helps in identifying metabolic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Resources
Search...