Genotyping Array Service
The genotyping array is a powerful tool to detect common single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), copy number variations (CNVs), and other genetic variations.
Background of Genotyping Array
One of the main objectives of human genetics is to find DNA variations that cause disease. It is necessary to be able to evaluate DNA sequence variation on a genome-wide scale in order to locate these causative loci. On two homologous chromosomes, the majority of genomic locations share the same base residues between individuals. The remaining genes encode variations in human variability, including varying susceptibilities to disease. SNPs are the regions of the genome that contain two different nucleotide residues. SNPs make up a sizable portion of these DNA variations in the majority of the human population. The human genome is thought to have 10 million SNPs.
Utilizing carefully chosen tagging SNPs, genotyping arrays offer unrivaled genome coverage, increasing the chance of finding real connections for a particular phenotype. The intrinsic connection between the markers that make up haplotype blocks, which enables one highly correlated marker to serve as a proxy for several other markers in the genome, is what gives the tagging SNP technique its power. This method enables optimal genome-wide coverage of both common and rare variants by allowing for the widest selection of the most informative markers.
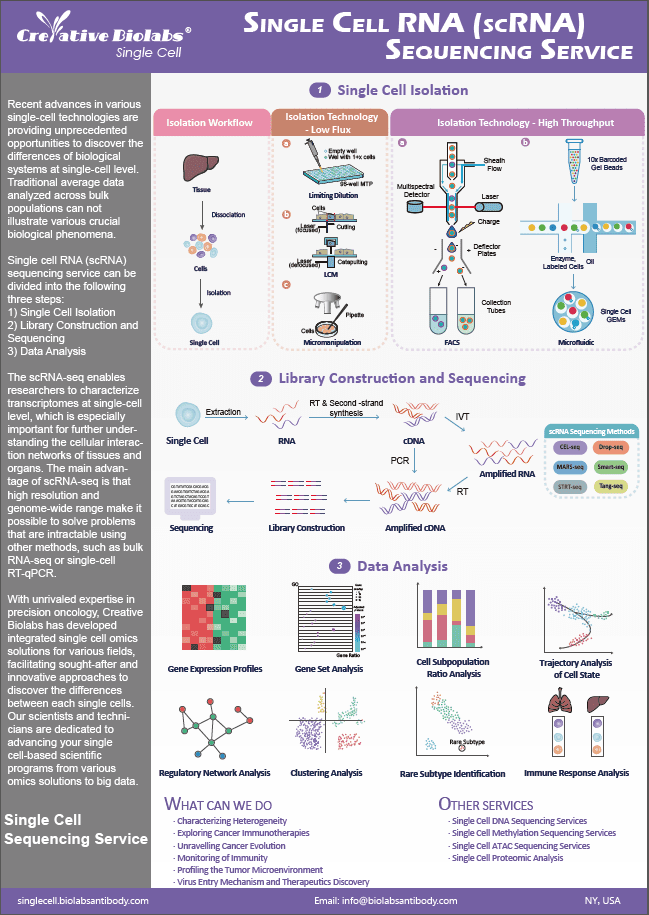
 Fig.1 Workflow of the genotyping array. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.1 Workflow of the genotyping array. (Creative Biolabs)
Applications of Genotyping Array
- Genome-wide genotyping for complex disease research, clinical applications, or pharmacology.
- Specific genotyping (psychological, immunological, tumor arrays).
- Microbiome research.
- Agrigenomics.
- Customed genes analysis.
Our Featured Genotyping Array Services
The genotyping array services provided by Creative Biolabs enable researchers to conduct genome-wide and phenotype-wide association studies. Our genotyping array service provides superior data quality and dense genome coverage for detecting CNVs and SNPs.
Our genotyping array service provides researchers with the flexibility to genotype samples containing hundreds of thousands to millions of markers that provide genome-wide coverage with the most recent content.
Additionally, we have modified protocols for the treatment of partially degraded samples from archival tissues, including formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues. Our robust software includes numerous third-party plug-ins for both genotyping and CNV analysis, as well as the capability to simultaneously analyze SNPs and CNV probes for downstream analysis. For more information, please contact us.
Published Data
| Paper Title | A customized and versatile high-density genotyping array for the mouse |
| Journal | Nature Methods |
| Published | 2009 |
| Abstract | They created a high-density mouse genotyping array with 623,124 single-nucleotide polymorphisms that represent the known genetic variation in laboratory mice. In addition, the array includes 916,269 invariant genomic probes targeted to functional elements and areas known to harbor segmental duplications. The array enables the study of genetic diversity, copy number variation, allele-specific gene expression, and DNA methylation. |
| Result | They evaluated the intensity of SNP and IGP probes on chromosome 17 between C57BL/6J and BALB/cByJ to assess the array's efficacy in detecting copy-number variation (CNV). The mouse diversity array reveals the presence of a previously documented 475 kb duplication in the BALB/cBy genome. They then used our array to examine 80 previously reported CNVs. They confirmed 83% (44) of these CNVs using their array, and 53 intervals could be matched to mouse genome assembly build 36. |
Features
-
High Throughput and Cost-Effective Analysis
Our genotyping array service offers high-throughput capabilities, allowing for the simultaneous analysis of thousands of samples. This efficiency makes it a cost-effective solution for large-scale genetic studies, enabling researchers to perform comprehensive genomic analyses within budget constraints.
-
Comprehensive Coverage
Our genotyping arrays offer extensive genomic coverage, with the ability to analyze over 90% of CpG loci across the entire genome. This comprehensive coverage ensures that significant genetic variations are detected, providing a thorough understanding of the genetic landscape.
-
Robust and Reliable Data
The genotyping arrays are designed to deliver robust and reliable data with minimal user intervention. The pre-optimized reagents and validated workflows ensure high-quality results, reducing the likelihood of errors and increasing the reproducibility of findings.
-
Automated Workflow
Our service includes an automated workflow that minimizes hands-on time, allowing for efficient sample processing. The end-to-end automation from target preparation to data analysis enhances productivity and reduces the potential for manual errors.
-
Customizable Content
The service provides fully customizable array content, accommodating specific research needs. Researchers can design arrays with proprietary markers or select from pre-validated markers, ensuring that the genotyping arrays are tailored to the unique requirements of their studies.
Q&As
Q: What types of samples can be used with the Genotyping Array Service?
A: The service can analyze DNA from a variety of sources, including blood, saliva, tissue, and cultured cells. The flexibility in sample types allows for a wide range of applications in both human and non-human research.
Q: How is data quality ensured in the Genotyping Array Service?
A: The service employs rigorous quality control measures, including high call rates and accuracy, with more than 80% of bases having a Q30 quality score. Automated workflows and pre-optimized reagents further enhance data reliability and reproducibility.
Q: What bioinformatics support is provided with the Genotyping Array Service?
A: Comprehensive bioinformatics support includes data analysis tools for SNP calling, copy number variation analysis, and functional annotation. This ensures that researchers can easily interpret and utilize the complex genetic data generated.
Q: How does the Genotyping Array Service handle high-throughput requirements?
A: The service offers high-throughput capabilities, processing thousands of samples simultaneously. Automated workflows and minimal hands-on time increase efficiency, making it suitable for large-scale genomic studies.
Q: What turnaround time can researchers expect from the Genotyping Array Service?
A: The Genotyping Array Service typically offers a rapid turnaround time, with results available within a few weeks. This quick processing allows researchers to make timely decisions and advance their studies efficiently.
Resources
Search...